Solution for Programming Exercise 6.8
This page contains a sample solution to one of the exercises from Introduction to Programming Using Java.
Exercise 6.8:
Write a program that has a JTextArea where the user can enter some text. Then program should have a button such that when the user clicks on the button, the panel will count the number of lines in the user's input, the number of words in the user's input, and the number of characters in the user's input. This information should be displayed on three labels. Recall that if textInput is a JTextArea, then you can get the contents of the JTextArea by calling the function textInput.getText(). This function returns a String containing all the text from the text area. The number of characters is just the length of this String. Lines in the String are separated by the new line character, '\n', so the number of lines is just the number of new line characters in the String, plus one. Words are a little harder to count. Exercise 3.4 has some advice about finding the words in a String. Essentially, you want to count the number of characters that are first characters in words. Don't forget to put your JTextArea in a JScrollPane, and add the scroll pane to the container, not the text area. Scrollbars should appear when the user types more text than will fit in the available area. Here is a picture of my solution:
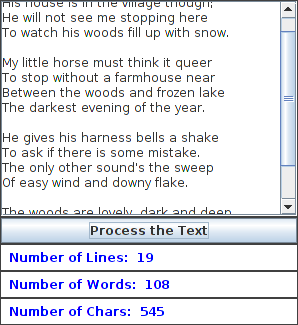
The panel contains five components. There are several ways to lay them out. A GridLayout with five rows certainly will not work, because the JTextArea should be taller than the other components. One possible layout is to use a GridLayout with two rows. The JTextArea would occupy the first row. The bottom half would contain a JPanel that holds the other four components. (A GridLayout with two columns and one row would also work, if you wanted a panel that was wider and not so tall. You could put the JTextArea in the left half and the other components in a JPanel in the right half.) However, I decided to use a BorderLayout. The JTextArea occupies the CENTER position, and the SOUTH position is occupied by a JPanel that contains the other components. The nested JPanel uses a GridLayout with four rows. My main() program sets the size of the window to 300-by-350, and the text area gets the space not occupied by the bottom panel. Once this choice has been made, writing the constructor is not hard.
I use an anonymous inner class to listen for ActionEvents from the button. The actionPerformed() method of the listener just calls a method named processInput() in the main class; this method does the real work. The processInput() method just has to get the text from the JTextArea, do the counting, and set the labels. The only interesting part is counting the words. Back in Exercise 3.4, words such as "can't", that contain an apostrophe, were counted as two words. This time around, let's handle this special case. Two letters with an apostrophe between them should be counted as part of the same word. The algorithm for counting words is still
wordCt = 0
for each character in the string:
if the character is the first character of a word:
Add 1 to wordCt
but testing whether a given character is the first character in a word has gotten a little more complicated. To make the test easier, I use a boolean variable, startOfWord. The value of this variable is set to true if the character is the start of a word and to false if not. That is, the algorithm becomes:
wordCt = 0
for each character in the string:
Let startOfWord be true if at start of word, false otherwise
if startOfWord is true:
Add 1 to wordCt
The use of a "flag variable" like startOfWord can simplify the calculation of a complicated boolean condition. The value is computed as a series of tests:
boolean startOfWord; // Is character i the start of a word?
if ( Character.isLetter(text.charAt(i)) == false )
startOfWord = false; // No. It's not a letter.
else if (i == 0)
startOfWord = true; // Yes. It's a letter at start of text.
else if ( Character.isLetter(text.charAt(i-1)) )
startOfWord = false; // No. It's a letter preceded by a letter.
else if ( text.charAt(i-1) == '\'' && i > 1
&& Character.isLetter(text.charAt(i-2)) )
startOfWord = false; // No. It's a continuation of a word
// after an apostrophe.
else
startOfWord = true; // Yes. It's a letter preceded by
// a non-letter.
The first test checks whether the character in position i is a letter. If it is not, then we know that it can't be the start of a word, so startOfWord is false. If it is a letter, it might be the start of a word, so we go on to make additional tests. Note that if we get to the other tests at all, we already know that the character in position i is a letter. And so on. This style of "cascading tests" is very useful. In each test, we already have all the information from the previous tests. Note that the cascade effect works only with "else if". Using "if" in place of "else if" in the preceding code would not give the right answer. (You should be sure to understand why this is so.) You should also note why the test if (i == 0) has to be made before the test if ( Character.isLetter(text.charAt(i-1)) ) -- it's because text.charAt(i-1) gives an index-out-of-bounds exception if i is zero.
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
import javax.swing.*;
/**
* In this panel, the user types some text in a JTextArea and presses
* a button. The panel computes and displays the number of lines
* in the text, the number of words in the text, and the number of
* characters in the text. A word is defined to be a sequence of
* letters, except that an apostrophe with a letter on each side
* of it is considered to be a letter. (Thus "can't" is one word,
* not two.)
*/
public class TextCounter extends JPanel {
/**
* A main routine allows this class to be run as an application.
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
JFrame window = new JFrame("Text Counter");
TextCounter content = new TextCounter();
window.setContentPane(content);
window.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
window.setLocation(120,70);
window.setSize(300,350);
window.setVisible(true);
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------
private JTextArea textInput; // For the user's input text.
private JLabel lineCountLabel; // For displaying the number of lines.
private JLabel wordCountLabel; // For displaying the number of words.
private JLabel charCountLabel; // For displaying the number of chars.
/**
* The constructor creates components and lays out the panel.
*/
public TextCounter() {
setBackground(Color.DARK_GRAY);
/* Create the text input area and make sure it has a
white background. */
textInput = new JTextArea();
textInput.setBackground(Color.WHITE);
/* Create a panel to hold the button and three display
labels. These will be laid out in a GridLayout with
4 rows and 1 column. */
JPanel south = new JPanel();
south.setBackground(Color.DARK_GRAY);
south.setLayout( new GridLayout(4,1,2,2) );
/* Create the button and a listener to listen for
clicks on the button, and add it to the panel. */
JButton countButton = new JButton("Process the Text");
countButton.addActionListener( new ActionListener() {
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent evt) {
processInput();
}
});
south.add(countButton);
/* Create each of the labels, set their colors, and
add them to the panel. */
lineCountLabel = new JLabel(" Number of lines:");
lineCountLabel.setBackground(Color.WHITE);
lineCountLabel.setForeground(Color.BLUE);
lineCountLabel.setOpaque(true);
south.add(lineCountLabel);
wordCountLabel = new JLabel(" Number of words:");
wordCountLabel.setBackground(Color.WHITE);
wordCountLabel.setForeground(Color.BLUE);
wordCountLabel.setOpaque(true);
south.add(wordCountLabel);
charCountLabel = new JLabel(" Number of chars:");
charCountLabel.setBackground(Color.WHITE);
charCountLabel.setForeground(Color.BLUE);
charCountLabel.setOpaque(true);
south.add(charCountLabel);
/* Use a BorderLayout on the panel. Although a BorderLayout
is the default, I want one with a vertical gap of two
pixels, to let the dark gray background color show through.
Also add a gray border around the panel. */
setLayout( new BorderLayout(2,2) );
setBorder(BorderFactory.createLineBorder(Color.DARK_GRAY));
/* The text area is put into a JScrollPane to provide
scroll bars for the TextArea, and the scroll pane is put in
the Center position. The panel that holds the button and
labels is in the South position. Note that the text area
will be sized to fill the space that is left after the
panel is assigned its preferred height. */
JScrollPane scroller = new JScrollPane( textInput );
add(scroller, BorderLayout.CENTER);
add(south, BorderLayout.SOUTH);
} // end constructor
/**
* This will be called by the action listener for the button when the user
* clicks the button. It gets the text from the text area, counts the number
* of chars, words, and lines that it contains, and sets the labels to
* display the results.
*/
public void processInput() {
String text; // The user's input from the text area.
int charCt, wordCt, lineCt; // Char, word, and line counts.
text = textInput.getText();
charCt = text.length(); // The number of characters in the
// text is just its length.
/* Compute the wordCt by counting the number of characters
in the text that lie at the beginning of a word. The
beginning of a word is a letter such that the preceding
character is not a letter. This is complicated by two
things: If the letter is the first character in the
text, then it is the beginning of a word. If the letter
is preceded by an apostrophe, and the apostrophe is
preceded by a letter, than its not the first character
in a word.
*/
wordCt = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < charCt; i++) {
boolean startOfWord; // Is character i the start of a word?
if ( Character.isLetter(text.charAt(i)) == false )
startOfWord = false; // No. It's not a letter.
else if (i == 0)
startOfWord = true; // Yes. It's a letter at start of text.
else if ( Character.isLetter(text.charAt(i-1)) )
startOfWord = false; // No. It's a letter preceded by a letter.
else if ( text.charAt(i-1) == '\'' && i > 1
&& Character.isLetter(text.charAt(i-2)) )
startOfWord = false; // No. It's a continuation of a word
// after an apostrophe.
else
startOfWord = true; // Yes. It's a letter preceded by
// a non-letter.
if (startOfWord)
wordCt++;
}
/* The number of lines is just one plus the number of times the
end of line character, '\n', occurs in the text. */
lineCt = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < charCt; i++) {
if (text.charAt(i) == '\n')
lineCt++;
}
/* Set the labels to display the data. */
lineCountLabel.setText(" Number of Lines: " + lineCt);
wordCountLabel.setText(" Number of Words: " + wordCt);
charCountLabel.setText(" Number of Chars: " + charCt);
} // end processInput()
} // end class TextCounter