Previous:Constructive Solid Geometry Main Index Next:Union
Most shape primitives, like spheres, boxes and blobs divide the world into two regions. One region is inside the object and one is outside. Given any point in space you can say it's either inside or outside any particular primitive object. Well, it could be exactly on the surface but this case is rather hard to determine due to numerical problems.
Even planes have an inside and an outside. By definition, the surface normal of the plane points towards the outside of the plane. You should note that triangles and triangle-based shapes cannot be used as solid objects in CSG since they have no well defined inside and outside.
CSG uses the concepts of inside and outside to combine shapes together as explained in the following sections.
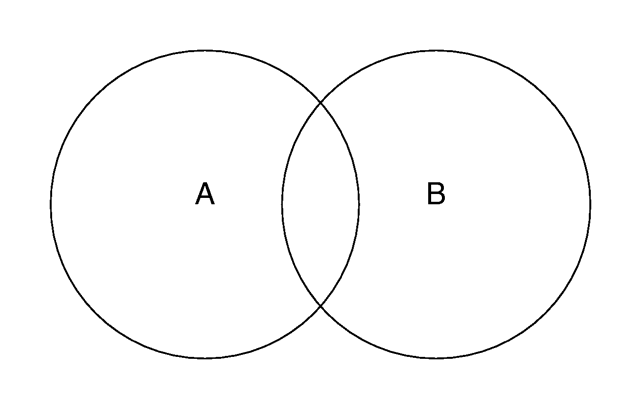
Imagine you have two objects that partially overlap like shown in the figure below. Four different areas of points can be distinguished: points that are neither in object A nor in object B, points that are in object A but not in object B, points that are not in object A but in object B and last not least points that are in object A and object B.

Two overlapping objects.
Keeping this in mind it will be quite easy to understand how the CSG operations work.
When using CSG it is often useful to invert an object so that it'll be inside-out. The appearance of the object is not changed, just the way that POV-Ray perceives it. When the inverse keyword is used the inside of the shape is flipped to become the outside and vice versa.
The inside/outside distinction is not important for a union, but is important for intersection, difference, and merge.Therefore any objects may be combined using union but only solid objects, i.e. objects that have a well-defined interior can be used in the other kinds of CSG. The objects described in "Finite Patch Primitives" have no well defined inside/outside. All objects described in the sections "Finite Solid Primitives" and "Infinite Solid Primitives".
Previous:Constructive Solid Geometry Main Index Next:Union